Google’s algorithms and the tools it provides for webmasters are always evolving. Recently, Google made a major change by removing the Page Experience Report from Search Console, a tool that many webmasters, SEO experts, and digital marketers had relied on for insights into user experience (UX) and overall website performance. This change left many questioning the reasoning behind it and what it means for the future of SEO.
In this blog post, we will delve into the five main reasons Google killed the Page Experience Report, explore its impact on search rankings, and offer guidance on how you can adapt your SEO strategy. Let’s explore why this happened and how you can continue to optimize your site for better website performance in the wake of this change.
What Was the Page Experience Report?
Before we dive into the reasons behind its removal, let’s take a look at what the Page Experience Report was. This report was introduced in Google Search Console to help website owners understand how well their site’s pages performed based on Core Web Vitals and other SEO metrics that directly impacted user experience (UX).
The Page Experience Report provided information about various performance metrics, including:
- Core Web Vitals (CWV): A set of three specific metrics used to evaluate how a page performs in terms of loading speed, interactivity, and visual stability.
- Mobile Usability: How well a website functions on mobile devices.
- HTTPS Security: Whether a website uses a secure connection.
- Intrusive Interstitials: Whether a site uses pop-ups or ads that could disrupt the user experience.
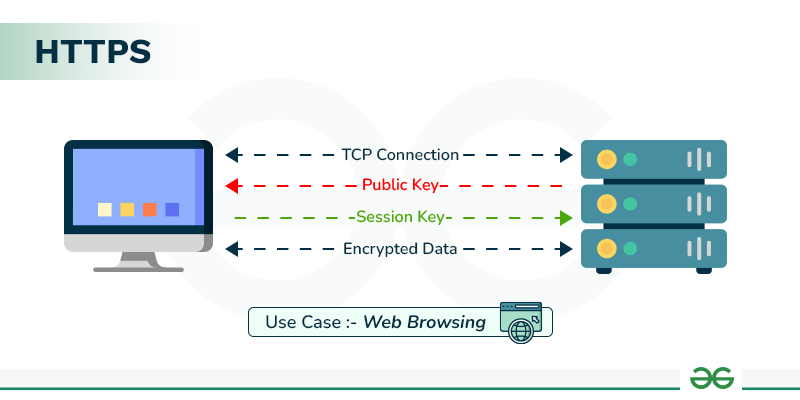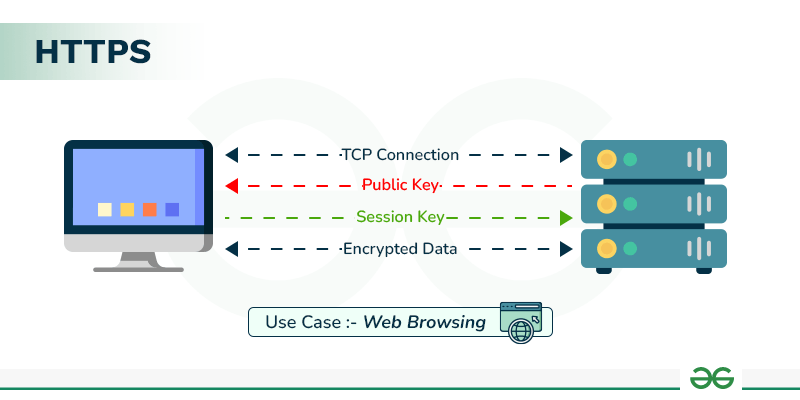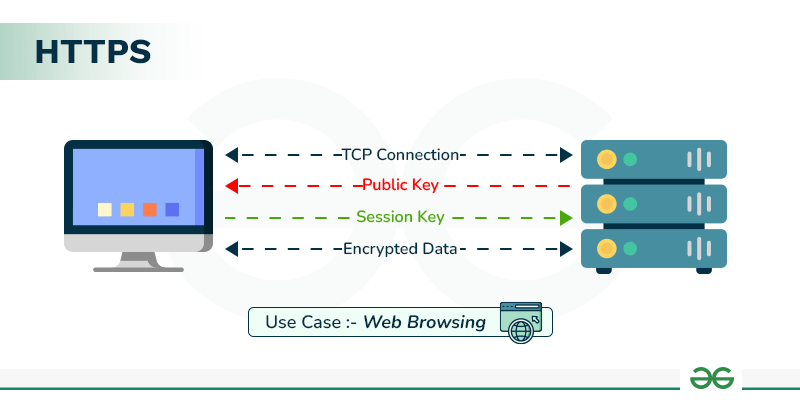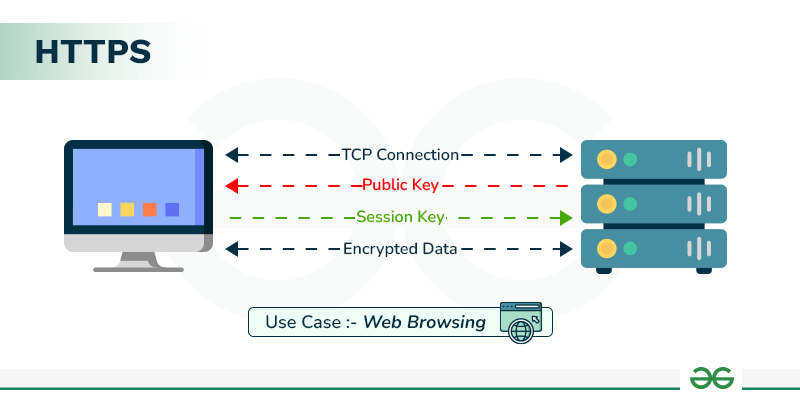
By analyzing these factors, Google provided website owners with an overview of how their site’s user experience (UX) could be impacting their SEO rankings.
However, as of now, Google has removed this report, which has raised many questions in the SEO community. Let’s explore the 5 key reasons why Google took this action.
1. Integration with Other Reports and Tools in Page Experience Report
How the Page Experience Report Became Redundant
One of the main reasons Google removed the Page Experience Report was the integration of its core metrics into other reports and tools. Google has streamlined the way it provides Core Web Vitals and SEO performance data by making these insights available within other existing tools such as Google Analytics, PageSpeed Insights, and the Core Web Vitals Report in Search Console.
- Core Web Vitals and Page Experience Report: Now available directly in Google Search Console, PageSpeed Insights, and Lighthouse, making it easier for users to access data about LCP, FID, and CLS.
- Performance Report: The Performance Report in Google Search Console also covers various metrics, including impressions, CTR, and more, offering a comprehensive look at how well your website is performing in search.
By consolidating these insights, Google has made it easier to track website performance and SEO metrics from a centralized location. The removal of the Page Experience Report reflects this shift, ensuring that SEO professionals and website owners can focus on actionable data from one place instead of relying on several different reports.
What This Means for Your SEO Strategy
While the Page Experience Report is gone, the need to focus on Core Web Vitals and website performance has not disappeared. In fact, it’s more important than ever to track these metrics through tools like PageSpeed Insights and Google Search Console to stay on top of your search rankings and user experience improvements.

2. A Shift Towards More Comprehensive Data
Combining User Experience with Overall Performance
Another reason Google removed the Page Experience Report is its focus on providing more comprehensive data. Instead of offering a specific report that focuses solely on user experience, Google is now integrating these insights into more complete and broader reports.
For instance, Core Web Vitals and other UX metrics are now considered in the Performance Report alongside more general metrics like CTR, impressions, and keyword rankings. This means that website owners can view both SEO metrics and user experience data in one cohesive report.
- User Experience: Beyond just loading speed, Google is now considering overall website performance and engagement, including user intent and how content matches that intent.
- Search Rankings: By incorporating Core Web Vitals into the overall SEO metrics, Google has acknowledged that website performance impacts rankings but is only one piece of the puzzle.
How to Leverage This Shift
Rather than viewing Core Web Vitals and user experience as separate from other ranking factors, website owners should now focus on the bigger picture. You can still improve your site’s user experience by ensuring fast loading times, mobile optimization, and minimal intrusive ads, but it’s equally important to enhance your content and backlink profile to boost your SEO rankings.
3. Over-Emphasis on UX Without Holistic SEO Strategy
Google’s Approach to Ranking Factors and Page Experience Report
The removal of the Page Experience Report also reflects a shift in Google’s approach to SEO. While user experience (UX) is a key ranking factor, it is not the only one. In the past, there was a risk that webmasters might focus too heavily on Core Web Vitals and mobile usability while neglecting other vital aspects of SEO like content relevance, keyword optimization, and backlinks.

By eliminating the report, Google might be signaling that SEO success requires a more balanced approach. It’s not enough to simply improve Core Web Vitals or mobile performance. To rank higher on Google, you need to optimize your site as a whole—focusing on both user experience and traditional SEO metrics such as:
- Content Quality: Ensure that your content is relevant, useful, and aligned with user intent.
- Backlink Building: High-quality backlinks remain one of the most important ranking factors for SEO.
- On-Page Optimization: Use proper keyword placement, meta descriptions, and structured data to boost your rankings.
Adapting Your SEO Strategy
To succeed in the new SEO environment, take a holistic approach to website optimization. Ensure that your site is optimized for mobile usability, loading speed, Core Web Vitals, and content quality. This will help you maintain high search rankings and improve user experience (UX) in the process.
4. The Changing Nature of Google’s Algorithm
Google’s Evolving Algorithm and SEO Priorities
Google’s algorithm is constantly evolving, and the company regularly introduces changes to improve the search experience. With the rise of AI and machine learning, the search engine is becoming increasingly adept at understanding user intent and delivering relevant content. This has led to a shift in SEO priorities.
Instead of focusing solely on specific metrics like Core Web Vitals, Google now considers a wide range of factors when determining search rankings. User experience is still a critical part of the algorithm, but it’s now integrated into a broader set of signals that include:
- Content Relevance: Google is better at understanding whether your content answers a user’s query.
- User Engagement: Signals like bounce rate, time on site, and pages per session now factor into rankings.
- Technical SEO: Site speed, security, and crawlability continue to be important for search rankings.
How to Stay Ahead with Google’s Algorithm Changes
To stay ahead of Google’s algorithm updates, make sure your site’s SEO is well-rounded. Focus on improving Core Web Vitals, but also ensure your content is high quality, your site is technically sound, and you’re building a strong backlink profile. Keep monitoring your SEO metrics and adjust your strategy to align with Google’s evolving standards.

5. Reducing Data Redundancy and User Confusion
Minimizing Unnecessary Reports and Metrics
Another factor that likely contributed to the removal of the Page Experience Report is the redundancy of the data it provided. Many of the insights offered in the report were already available in other tools, such as PageSpeed Insights and the Core Web Vitals Report in Search Console. Having multiple reports with overlapping data could have caused confusion for users and increased the complexity of using Google’s tools.
By eliminating the Page Experience Report, Google has streamlined its offerings, making it easier for website owners to find relevant performance data in one place.
Focusing on What Matters
With fewer reports to navigate, it’s now easier to focus on the key factors that matter for SEO. Instead of looking at separate reports for user experience, Core Web Vitals, and SEO performance, you can access everything from the Performance Report in Google Search Console.
FAQs
1. What happened to the Page Experience Report in Google Search Console?
Google has removed the Page Experience Report from Search Console as part of a broader effort to consolidate performance metrics into more comprehensive reports.
2. Does this mean Core Web Vitals no longer matter for SEO?
No, Core Web Vitals are still important for SEO. Google continues to use these metrics as part of its ranking factors, but the report for tracking them has been integrated into other tools like Google Analytics and the Performance Report.
3. Where can I find the Core Web Vitals data now?
You can now find Core Web Vitals data in the Core Web Vitals Report and Performance Report in Google Search Console or through other tools like PageSpeed Insights.
4. How do I continue optimizing for user experience without the Page Experience Report?
You can continue to optimize your site for user experience by focusing on Core Web Vitals, improving mobile usability, and ensuring that your site is fast, secure, and free from intrusive ads.
Conclusion: Adapting to Google’s Changes in SEO
Google’s decision to remove the Page Experience Report is a natural part of its ongoing efforts to improve the user experience for website owners and digital marketers. The key takeaway is that Core Web Vitals, user experience, and SEO metrics remain crucial for search rankings, but now they are integrated into other tools that provide a more holistic view of your site’s performance.
To succeed in the evolving landscape of SEO, continue to monitor your site’s Core Web Vitals, website performance, and SEO metrics through Google Search Console and other tools. A balanced SEO strategy that prioritizes both technical performance and content quality will ensure that your site ranks well and delivers an optimal user experience.

Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://www.binance.com/ph/register?ref=B4EPR6J0